Forms of Energy and Energy Conversion
Please read the text and then answer the questions below!
Energy: Forms and
Conversion
1. Forms of Energy
Energy exists in various forms, each with its unique
characteristics. Here are the main forms/types of energy:
a. Light Energy
Light energy allows us to see things around us. It comes
from sources like the sun, light bulbs, and flames.
b. Heat/Thermal Energy
Heat or thermal energy is what makes objects warm or
hot. Imagine feeling the warmth of a cozy blanket or a cup of hot cocoa.
c. Sound Energy
Sound energy is what we hear. When you clap your hands
or play a musical instrument, you are creating sound energy.
d. Electrical Energy
Electrical energy powers our devices. It flows through
wires and makes things like light bulbs, TVs, and computers work.
e. Kinetic Energy
Kinetic
energy is the energy of moving objects. When you ride a bike, kick a soccer
ball, or swing on a swing, you are using kinetic energy.
f. Potential Energy
Potential energy is stored energy. It's waiting to be
used! There are different forms/types of potential energy:
1. Chemical Potential Energy: Stored
in things like food or batteries.
2. Gravitational Potential Energy: Think
of a ball at the top of a hill—it has potential energy because it can roll
down.
3. Elastic Potential Energy: Found
in things like stretched rubber bands or a coiled spring.
When
you combine potential energy with kinetic energy, you get mechanical energy!
When you swing back and forth, you have both potential energy and kinetic
energy (mechanical energy). At the highest point of the swing, you have maximum
potential energy. As you swing down, that potential energy is converted into
kinetic energy—the energy of motion!
Mechanical energy refers to the energy associated with motion and position. Let’s break it down:
Kinetic Energy (Energy of Motion):
- Kinetic energy is the energy an object possesses due to its movement. When something is in motion, it has kinetic energy.
- For example, a moving car, a spinning top, or a bouncing ball all have kinetic energy.
Potential Energy (Energy of Position):
- Potential energy is the energy stored in an object based on its position or height relative to the ground or another reference point.
- Different types of potential energy include:
- Gravitational Potential Energy: An object raised above the ground has potential energy due to gravity. Think of a ball at the top of a hill—it can roll down, converting potential energy into kinetic energy.
- Elastic Potential Energy: Stretched rubber bands, compressed springs, or coiled ropes store energy that can be released when they return to their original shape.
- Chemical Potential Energy: Stored in food, batteries, or fuels. When these substances react, their potential energy can be converted into other forms (like heat or light).
Mechanical Energy (Combination of Kinetic and Potential Energy):
- Mechanical energy is the sum of kinetic energy and potential energy. When you swing on a swing, for instance, you experience both kinetic energy as you move and potential energy at the highest point of the swing.
2. Conversion/Change of Energy
Energy can convert/change from one form to another. This
process is called energy conversion. Here are some examples:
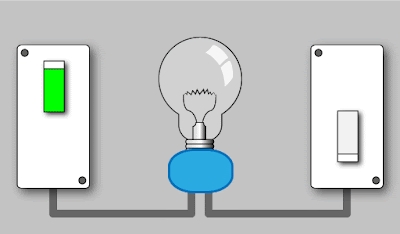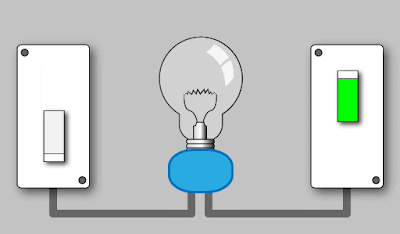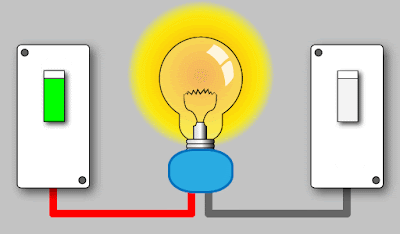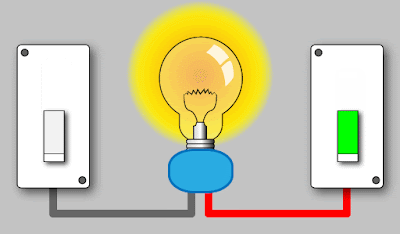
a. Turning
on a Light Bulb:
Electrical energy → Light energy
b. Rubbing
Your Hands Together:
Mechanical energy (from rubbing) → Heat energy (your
hands feel warmer)
c. Swinging
on a Swing:
Potential energy (at the highest point) → Kinetic energy
(as you swing down)
Remember, energy is all around us, and understanding its different forms helps us appreciate the world better!
Now, let's do the homework!









.gif)